- Published on
- •👁️
JPA N+1 문제 해결에 따른 성능 변화 분석 - 3. 테스트 환경 및 조건
- Authors

- Name
- River
목차 페이지로 이동
데이터 규모에 따른 JPA N+1 문제 진단과 해결 전략 비교
(Fetch Join, Entity Graph, Batch Fetching)
목차
(1)Database Seeding
주요 엔티티 관계도
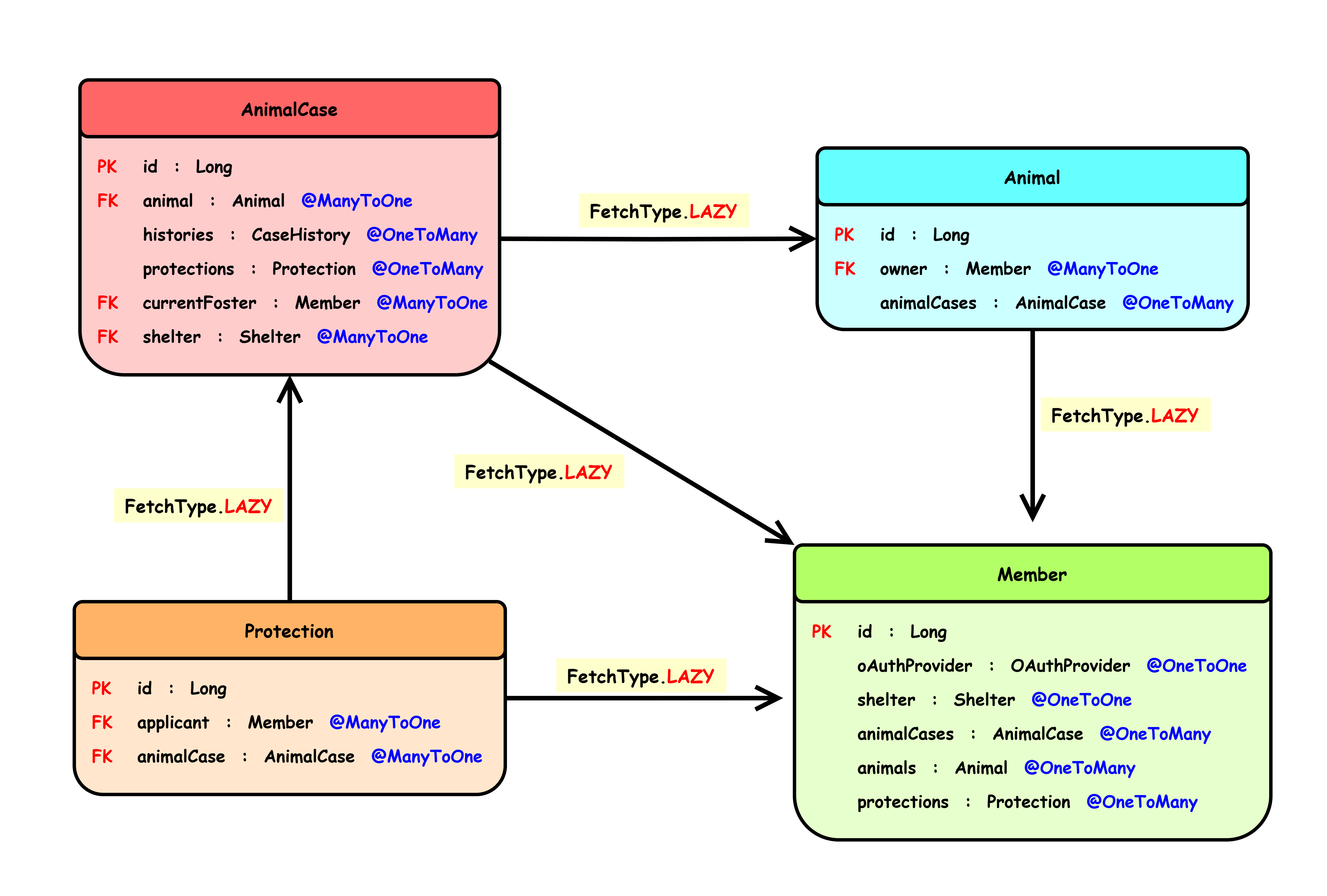
- Member : 회원
- Animal : 동물
- AnimalCase : 동물 이력 관리
- Protection : 임시보호/입양 신청
소규모 데이터
- Member : 100명
- Animal : 100마리
- AnimalCase : 200개 (Member 당 2개)
- Protection : 100,000개 (AnimalCase 당 500개)
대규모 데이터
- Member : 500명
- Animal : 1000마리
- AnimalCase : 1000개 (Member 당 2개)
- Protection : 1,000,000 개 (AnimalCase 당 1000개)
(1)직접 개발한 API 전체
AnimalCase API (동물 이력 케이스)
GET /api/v1/animal-cases - 동물 케이스 목록 조회
GET /api/v1/animal-cases/\{caseId} - 동물 케이스 상세 조회
GET /api/v1/animal-cases/animals/{animalId} - 동물 ID로 케이스 ID 조회
Facility API (병원/보호소 시설)
GET /api/v1/facilities - 보호소/병원 목록 조회
GET /api/v1/facilities/shelters - 보호소 목록 조회
GET /api/v1/facilities/hospitals - 병원 목록 조회
GET /api/v1/facilities/map - 반경 내 보호소/병원 조회
GET /api/v1/facilities/shelters/map - 반경 내 보호소 조회
GET /api/v1/facilities/hospitals/map - 반경 내 병원 조회
KakaoMap API (좌표 ⇒ 주소 전환)
GET /api/v1/maps/address - 좌표를 주소로 변환
Protection API (입양/임시보호 신청)
GET /api/v1/protections - 임시보호/입양 대기 동물 목록
GET /api/v1/protections/\{caseId} - 임시보호/입양 대기 동물 상세
POST /api/v1/protections - 임시보호/입양 동물 등록
PUT /api/v1/protections/\{caseId} - 임시보호/입양 동물 정보 수정
PATCH /api/v1/protections/\{caseId} - 임시보호/입양 동물 삭제
GET /api/v1/protections/my-cases - 내가 등록한 임시보호/입양 동물 목록
GET /api/v1/protections/my-protections - 내가 신청한 임시보호/입양 신청 목록
GET /api/v1/protections/shelter-cases/{shelterId} - 보호소의 보호 동물 목록
POST /api/v1/protections/\{caseId}/apply - 임시보호/입양 신청
PATCH /api/v1/protections/{protectionId}/cancel - 임시보호/입양 신청 취소
PATCH /api/v1/protections/{protectionId}/accept - 임시보호/입양 신청 수락
PATCH /api/v1/protections/{protectionId}/reject - 임시보호/입양 신청 거절
(2)후보 API 테스트
측정에 적합한 API endpoint 후보 선정
- 조회가 많고 지연 로딩/즉시 로딩이 많이 발생할 수 있는 GET API 선정
1. GET /api/v1/protections/my-protections - 내가 신청한 임시보호/입양 신청 목록 2. GET /api/v1/animal-cases/animals/{animalId} - 동물 ID로 케이스 ID 조회 3. GET /api/v1/animal-cases - 동물 케이스 목록 조회 4. GET /api/v1/animal-cases/\{caseId} - 동물 케이스 상세 조회 5. GET /api/v1/protections/shelter-cases/{shelterId} - 보호소의 보호 동물 목록 6. GET /api/v1/protections - 임시보호/입양 대기 동물 목록 7. GET /api/v1/protections/\{caseId} - 임시보호/입양 대기 동물 상세 8. GET /api/v1/protections/my-cases - 내가 등록한 임시보호/입양 동물 목록
대규모 데이터 환경에서 API 간단 테스트 (Batch Fetching : X)
GET /api/v1/protections/{caseId} - 임시보호/입양 대기 동물 상세
- 실행 속도 : 1868 ms
- JDBC 문장 수 : 1503
GET /api/v1/protections/my-cases - 내가 등록한 임시보호/입양 동물 목록
- 실행 속도 : 1544 ms
- JDBC 문장 수 : 1506
나머지 API는 100 ms 이하의 실행 속도를 나타냈으며 JDBC 문장 수 역시 낮은 수준 발생
최종 선정 결과
조건
Member, Animal, AnimalCase, Protection 테스트 데이터 구성에 알맞아야 한다.
Collection 연관 데이터가 많을 때 지연 로딩이 어떻게 성능에 작용하는지 보기 위함이다.
⇒ 즉, AnimalCase를 조회하면서 Protection 데이터도 사용해야 한다.
결과
1. GET /api/v1/protections/my-cases - 내가 등록한 임시보호/입양 동물 목록 2. GET /api/v1/protections/\{caseId} - 임시보호/입양 대기 동물 상세나머지 것은 Protection 자체를 조회하거나 AnimalCase만 조회하는 경우가 많았기에
방대한 양의 Protection 데이터의 영향이 없었다.
각 AnimalCase 당 1000개의 Protection 연관 데이터를 잘 보여줄 수 있는 것을 선정함.
(3)해당 API endpoint의 메서드 호출 과정
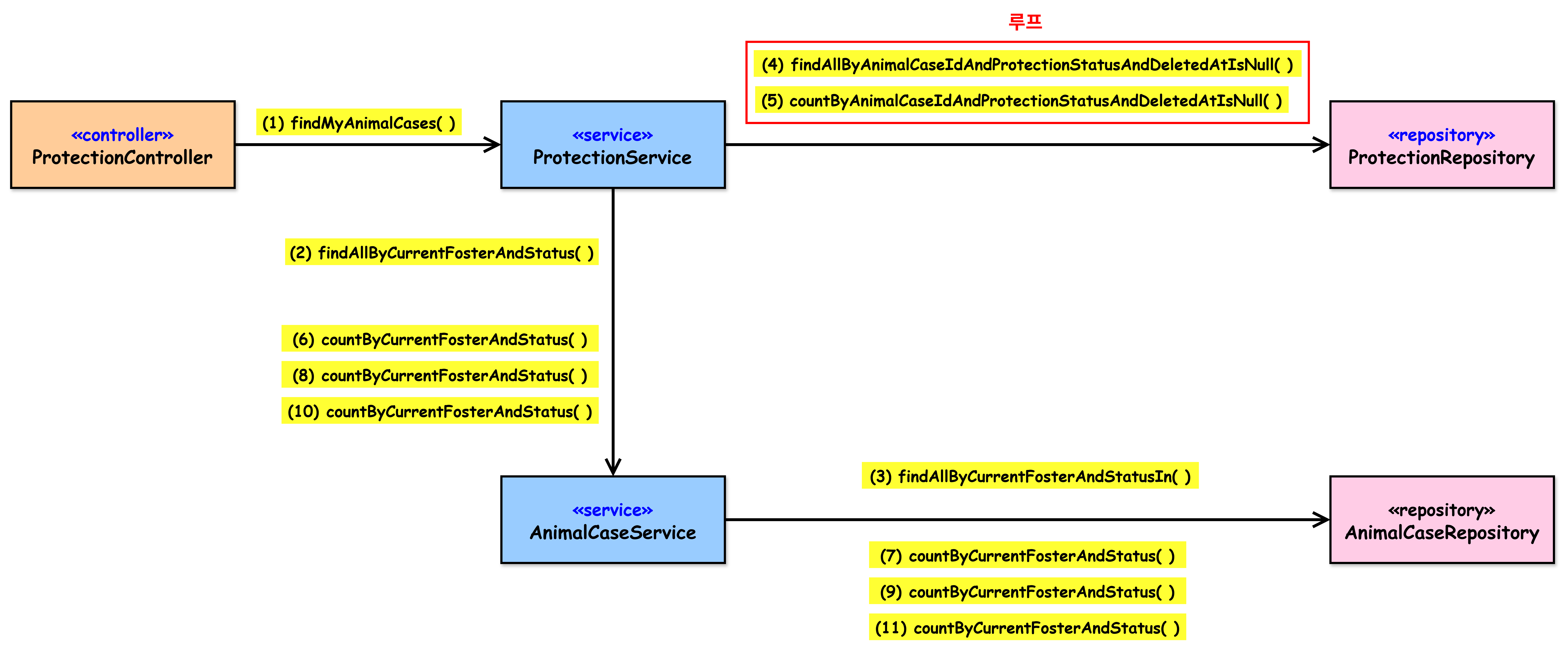
ProtectionService
public MyAnimalCasePageResponse findMyAnimalCases(Member currentFoster, Pageable pageable) {
Page<AnimalCase> cases = animalCaseService.findAllByCurrentFosterAndStatus(
currentFoster, List.of(
CaseStatus.PROTECT_WAITING,
CaseStatus.TEMP_PROTECTING,
CaseStatus.SHELTER_PROTECTING
), pageable
);
Page<MyAnimalCaseResponse> myAnimalCaseResponses = cases.map(animalCase -> {
List<PendingProtectionResponse> pendingProtections = getPendingProtections(animalCase.getId());
int pendingCount = protectionRepository.countByAnimalCaseIdAndProtectionStatusAndDeletedAtIsNull(
animalCase.getId(), ProtectionStatus.PENDING);
return MyAnimalCaseResponse.of(animalCase, pendingCount, pendingProtections);
});
long totalWaitingCount = animalCaseService.countByCurrentFosterAndStatus(
currentFoster, CaseStatus.PROTECT_WAITING);
long totalProtectingCount = animalCaseService.countByCurrentFosterAndStatus(
currentFoster, CaseStatus.TEMP_PROTECTING);
long shelterCount = animalCaseService.countByCurrentFosterAndStatus(
currentFoster, CaseStatus.SHELTER_PROTECTING);
return MyAnimalCasePageResponse.create(
myAnimalCaseResponses, currentFoster.getRole(), totalWaitingCount, totalProtectingCount, shelterCount
);
}
private List<PendingProtectionResponse> getPendingProtections(Long animalCaseId) {
return protectionRepository
.findAllByAnimalCaseIdAndProtectionStatusAndDeletedAtIsNull(animalCaseId, ProtectionStatus.PENDING)
.stream()
.map(PendingProtectionResponse::of)
.toList();
}
- (1) findMyAnimalCases( )
AnimalCaseService
public Page<AnimalCase> findAllByCurrentFosterAndStatus(
Member currentFoster, Collection<CaseStatus> statuses, Pageable pageable
) {
return animalCaseRepository.findAllByCurrentFosterAndStatusIn(currentFoster, statuses, pageable);
}
public long countByCurrentFosterAndStatus(Member currentFoster, CaseStatus caseStatus) {
return animalCaseRepository.countByCurrentFosterAndStatus(
currentFoster, caseStatus
);
}
- (2) findAllByCurrentFosterAndStatus( )
- (6) countByCurrentFosterAndStatus( )
- (8) countByCurrentFosterAndStatus( )
- (10) countByCurrentFosterAndStatus( )
ProtectionRepository
@Query("SELECT p FROM Protection p " +
"JOIN FETCH p.applicant " +
"WHERE p.animalCase.id = :animalCaseId " +
"AND p.protectionStatus = :status " +
"AND p.deletedAt IS NULL")
List<Protection> findAllByAnimalCaseIdAndProtectionStatusAndDeletedAtIsNull(
@Param("animalCaseId") Long animalCaseId,
@Param("status") ProtectionStatus status);
int countByAnimalCaseIdAndProtectionStatusAndDeletedAtIsNull(Long id, ProtectionStatus protectionStatus);
- 루프
- (4) getPendingProtections( ) ⇒ findAllByAnimalCaseIdAndProtectionStatusAndDeletedAtIsNull( )
- (5) countByAnimalCaseIdAndProtectionStatusAndDeletedAtIsNull( )
AnimalCaseRepository
@Query(value = "SELECT ac FROM AnimalCase ac " +
"LEFT JOIN FETCH ac.animal " +
"LEFT JOIN FETCH ac.currentFoster " +
"WHERE ac.currentFoster = :currentFoster AND ac.status IN :statuses AND ac.deletedAt IS NULL",
countQuery = "SELECT COUNT(ac) FROM AnimalCase ac WHERE ac.currentFoster = :currentFoster AND ac.status IN :statuses AND ac.deletedAt IS NULL")
Page<AnimalCase> findAllByCurrentFosterAndStatusIn(
@Param("currentFoster") Member currentFoster,
@Param("statuses") Collection<CaseStatus> statuses,
Pageable pageable
);
long countByCurrentFosterAndStatus(Member currentFoster, CaseStatus caseStatus);
- (3) findAllByCurrentFosterAndStatusIn( )
- (7) countByCurrentFosterAndStatus( )
- (9) countByCurrentFosterAndStatus( )
- (11) countByCurrentFosterAndStatus( )
(1)GET /api/v1/protections/my-cases
Original 버전
프로젝트 마지막 상태로 hibernate default batch size = 100으로 설정되어 있고, 테스트 데이터가 작아서 잘못된 것을 알지 못함
일부 Fetch Join이 적용된 상태
@Query(value = "SELECT ac FROM AnimalCase ac " + "LEFT JOIN FETCH ac.animal " + "LEFT JOIN FETCH ac.currentFoster " + "WHERE ac.currentFoster = :currentFoster AND ac.status IN :statuses AND ac.deletedAt IS NULL", countQuery = "SELECT COUNT(ac) FROM AnimalCase ac WHERE ac.currentFoster = :currentFoster AND ac.status IN :statuses AND ac.deletedAt IS NULL") Page<AnimalCase> findAllByCurrentFosterAndStatusIn( @Param("currentFoster") Member currentFoster, @Param("statuses") Collection<CaseStatus> statuses, Pageable pageable );- Member를 사용하지 않았지만 습관적으로 Fetch Join을 하여 오히려 성능 하락을 한 예시이다.
- Member를 가져오게 되면서 자동으로 Member의 @OneToOne 관계에 대한 쿼리가 추가되었다.
Pure 버전
Fetch Join, EntityGraph와 성능 비교를 위해서 루프 내 반복되는 쿼리나 코드 레벨에서 최적화가 필요한 부분을 개선한 버전이다.
즉, Fetch Join이나 EntityGraph 버전에서 해당 전략만 적용되지 않는 버전
⇒ 순수하게 N+1 문제 해결 전략의 영향만 비교
이렇게 설정한 다른 이유는 추후 Batch Fetching을 도입 시 Pure 버전만 영향을 받아서 성능 비교도 할 수 있기 때문이다.
특정 상태에 대한 쿼리문을 여러 번 조회하는 것 대신 GROUP BY와 IN을 활용하여 개선
long totalWaitingCount = animalCaseService.countByCurrentFosterAndStatus( currentFoster, CaseStatus.PROTECT_WAITING); long totalProtectingCount = animalCaseService.countByCurrentFosterAndStatus( currentFoster, CaseStatus.TEMP_PROTECTING); long shelterCount = animalCaseService.countByCurrentFosterAndStatus( currentFoster, CaseStatus.SHELTER_PROTECTING);Map<CaseStatus, Long> statusCountMap = new EnumMap<>(CaseStatus.class); List<Object[]> statusCounts = animalCaseService.countAllByCurrentFosterAndStatuses( currentFoster, List.of(CaseStatus.PROTECT_WAITING, CaseStatus.TEMP_PROTECTING, CaseStatus.SHELTER_PROTECTING) ); for (Object[] result : statusCounts) { statusCountMap.put((CaseStatus) result[0], (Long) result[1]); } long totalWaitingCount = statusCountMap.getOrDefault(CaseStatus.PROTECT_WAITING, 0L); long totalProtectingCount = statusCountMap.getOrDefault(CaseStatus.TEMP_PROTECTING, 0L); long shelterCount = statusCountMap.getOrDefault(CaseStatus.SHELTER_PROTECTING, 0L);루프 내 반복되는 쿼리 최적화 (명시적으로 IN 사용)
⇒ AnimalCase의 ID를 루프 내에서 반복 조회하던 것을 IN을 활용하여 한 번에 조회
List<Long> caseIds = cases.getContent().stream().map(AnimalCase::getId).toList(); List<Protection> allPendingProtections = protectionRepository .findAllByAnimalCaseIdsAndProtectionStatusAndDeletedAtIsNull(caseIds, ProtectionStatus.PENDING);
Optimized 버전
Pure 버전에서 Fetch Join을 적용한 버전이다.
Fetch Join 최적화 적용
@Query(value = "SELECT ac FROM AnimalCase ac " + "JOIN FETCH ac.animal " + "WHERE ac.currentFoster = :currentFoster AND ac.status IN :statuses AND ac.deletedAt IS NULL", countQuery = "SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT ac) FROM AnimalCase ac WHERE ac.currentFoster = :currentFoster AND ac.status IN :statuses AND ac.deletedAt IS NULL") Page<AnimalCase> findAllByCurrentFosterAndStatusIn( @Param("currentFoster") Member currentFoster, @Param("statuses") Collection<CaseStatus> statuses, Pageable pageable ); @Query("SELECT DISTINCT p FROM Protection p " + "JOIN FETCH p.animalCase " + "JOIN FETCH p.applicant m " + "LEFT JOIN FETCH m.shelter " + "LEFT JOIN FETCH m.oAuthProvider " + "WHERE p.animalCase.id IN :animalCaseIds " + "AND p.protectionStatus = :status " + "AND p.deletedAt IS NULL") List<Protection> findAllByAnimalCaseIdsAndProtectionStatusAndDeletedAtIsNull( @Param("animalCaseIds") List<Long> animalCaseIds, @Param("status") ProtectionStatus status );findAllByCurrentFosterAndStatusIn()은 Original 버전과 달리 Fetch Join으로 Animal만 가져온다.⇒ 이는 이후 코드에서 Animal의 경우 사용되나 Member는 사용하지 않기 때문이다.
JOIN FETCH p.applicant m이므로 Member의 @OneToOne인 Shetler와 OAuthProvider 역시 같이 가져와야 추가적인 쿼리가 발생하지 않는다.
Graph 버전
- Pure 버전에서 EntityGraph를 적용한 버전이다.
테스트 케이스 1
- 소규모 데이터
- K6 부하 테스트 시 동시 접속자 최대 100명 (동일한 환경에서 테스트 하기 위해서)
default_batch_fetch_size: 0
테스트 케이스 2
- 대규모 데이터
- K6 부하 테스트 시 동시 접속자 최대 100명
default_batch_fetch_size: 0
테스트 케이스 3
- 대규모 데이터
- K6 부하 테스트 시 동시 접속자 최대 100명
default_batch_fetch_size: 100
애플리케이션 설정
- Java 21
- Spring Boot 3.4.2
- Connection Pool = 10 (기본값 유지)
- Thread Pool (기본값 유지)
데이터 베이스
- MySQL 8.0 (로컬)
다음 페이지로 이동 (4-1. 테스트 결과 1)